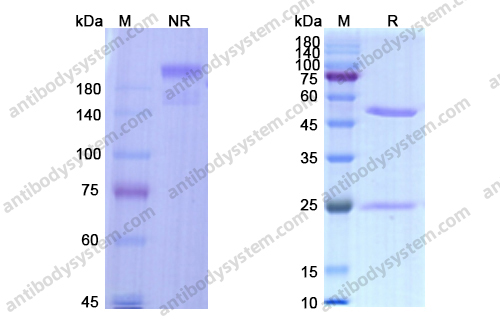
Catalog No.
DXX00102
Expression system
Mammalian Cells
Species reactivity
Staphylococcus aureus
Host species
Human
Isotype
IgG1-kappa
Clonality
Monoclonal
Target
Alpha-hemolysin, hly, Alpha-HL, Alpha-toxin, hla
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Purification
Protein A/G purified from cell culture supernatant.
Accession
P09616
Applications
Research Grade Biosimilar
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Store at 4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Store at -20°C 12 months. Store at -80°C long term.
Alternative Names
MEDI4893, CAS: 1629620-18-3
Clone ID
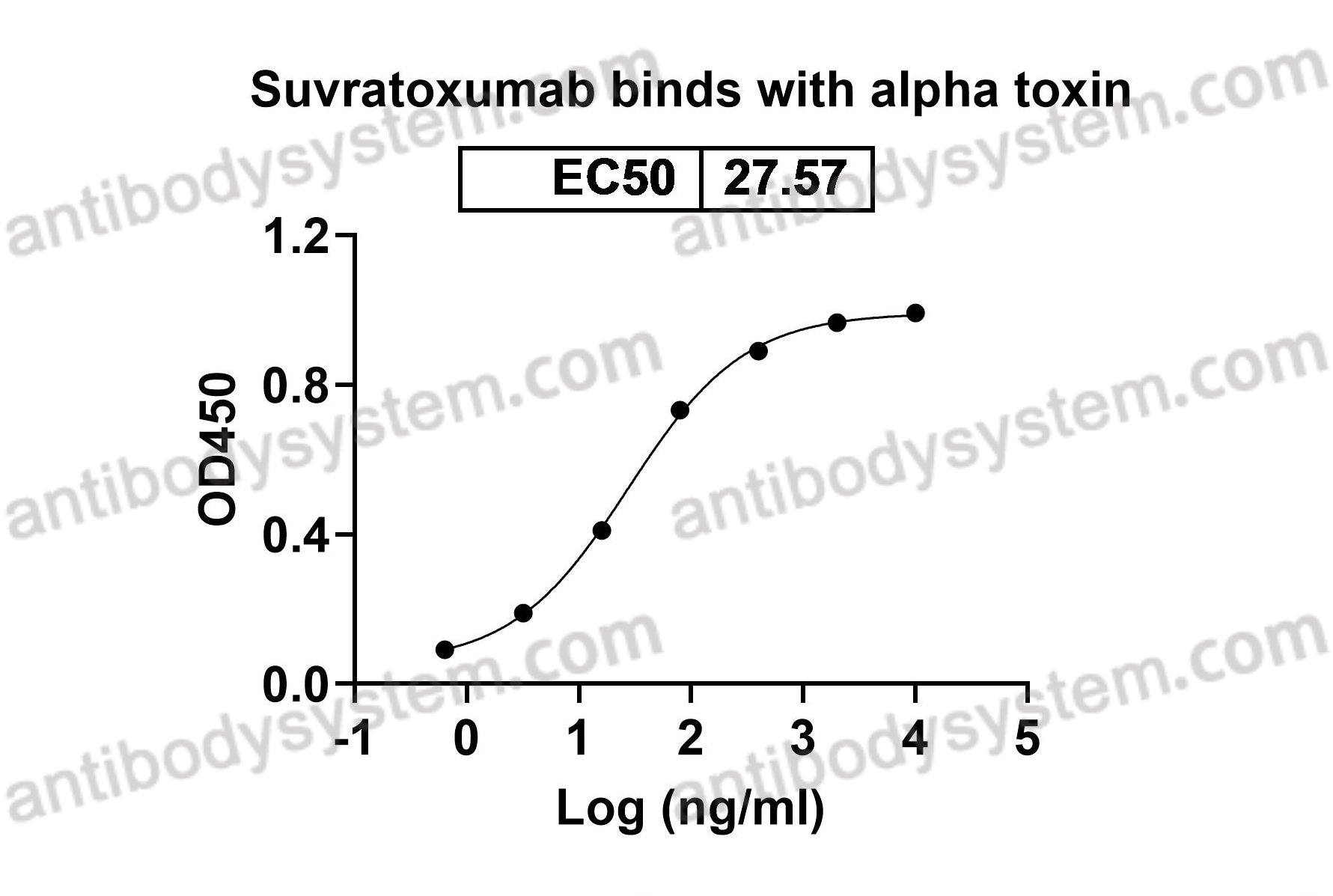
Suvratoxumab
α-Toxin Induces Platelet Aggregation and Liver Injury during Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis, PMID: 30033122
Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis of the MEDI4893 (Suvratoxumab) Epitope Reduces Alpha Toxin Lytic Activity In Vitro and Staphylococcus aureus Fitness in Infection Models, PMID: 30150481
Efficacy and safety of suvratoxumab for prevention of Staphylococcus aureus ventilator-associated pneumonia (SAATELLITE): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 pilot trial, PMID: 33894131
Development of a mechanism of action reflective and robust potency assay for a therapeutic antibody against alpha toxin using rabbit erythrocytes, PMID: 33075362
Staphylococcus aureus drives expansion of low-density neutrophils in diabetic mice, PMID: 30985291
Efficacy of a Multimechanistic Monoclonal Antibody Combination against Staphylococcus aureus Surgical Site Infections in Mice, PMID: 31138566
Mechanisms of neutralization of a human anti-α-toxin antibody, PMID: 25210036
Survival during influenza-associated bacterial superinfection improves following viral- and bacterial-specific monoclonal antibody treatment, PMID: 31341107
MEDI4893* Promotes Survival and Extends the Antibiotic Treatment Window in a Staphylococcus aureus Immunocompromised Pneumonia Model, PMID: 25987629
Multimechanistic Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbs) Targeting Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin and Clumping Factor A: Activity and Efficacy Comparisons of a MAb Combination and an Engineered Bispecific Antibody Approach, PMID: 28584141
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI4893, an Investigational, Extended-Half-Life, Anti-Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Human Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Adults, PMID: 27795368
Anti-alpha-toxin monoclonal antibody and antibiotic combination therapy improves disease outcome and accelerates healing in a Staphylococcus aureus dermonecrosis model, PMID: 25348518
Critical Role of Alpha-Toxin and Protective Effects of Its Neutralization by a Human Antibody in Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections, PMID: 27401576
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Is Conserved among Diverse Hospital Respiratory Isolates Collected from a Global Surveillance Study and Is Neutralized by Monoclonal Antibody MEDI4893, PMID: 27324766
The characteristics of pre-existing humoral imprint determine efficacy of S. aureus vaccines and support alternative vaccine approaches., PMID:38232694
Performance of the Cepheid Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus/S. aureus Skin and Soft Tissue Infection PCR Assay on Respiratory Samples from Mechanically Ventilated Patients for S. aureus Screening during the Phase 2 Double-Blind SAATELLITE Study., PMID:35758652
Efficacy and safety of suvratoxumab for prevention of Staphylococcus aureus ventilator-associated pneumonia (SAATELLITE): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 pilot trial., PMID:33894131
Development of a mechanism of action reflective and robust potency assay for a therapeutic antibody against alpha toxin using rabbit erythrocytes., PMID:33075362
A Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model for the Prediction of "Half-Life Extension" and "Catch and Release" Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics., PMID:32697437
Survival during influenza-associated bacterial superinfection improves following viral- and bacterial-specific monoclonal antibody treatment., PMID:31341107
Efficacy of a Multimechanistic Monoclonal Antibody Combination against Staphylococcus aureus Surgical Site Infections in Mice., PMID:31138566
Staphylococcus aureus drives expansion of low-density neutrophils in diabetic mice., PMID:30985291
Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis of the MEDI4893 (Suvratoxumab) Epitope Reduces Alpha Toxin Lytic Activity In Vitro and Staphylococcus aureus Fitness in Infection Models., PMID:30150481
α-Toxin Induces Platelet Aggregation and Liver Injury during Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis., PMID:30033122
Multimechanistic Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbs) Targeting Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin and Clumping Factor A: Activity and Efficacy Comparisons of a MAb Combination and an Engineered Bispecific Antibody Approach., PMID:28584141
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI4893, an Investigational, Extended-Half-Life, Anti-Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Human Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Adults., PMID:27795368
Critical Role of Alpha-Toxin and Protective Effects of Its Neutralization by a Human Antibody in Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections., PMID:27401576
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Is Conserved among Diverse Hospital Respiratory Isolates Collected from a Global Surveillance Study and Is Neutralized by Monoclonal Antibody MEDI4893., PMID:27324766
MEDI4893* Promotes Survival and Extends the Antibiotic Treatment Window in a Staphylococcus aureus Immunocompromised Pneumonia Model., PMID:25987629
Anti-alpha-toxin monoclonal antibody and antibiotic combination therapy improves disease outcome and accelerates healing in a Staphylococcus aureus dermonecrosis model., PMID:25348518
Mechanisms of neutralization of a human anti-α-toxin antibody., PMID:25210036