Catalog No.
KDD87601
Description
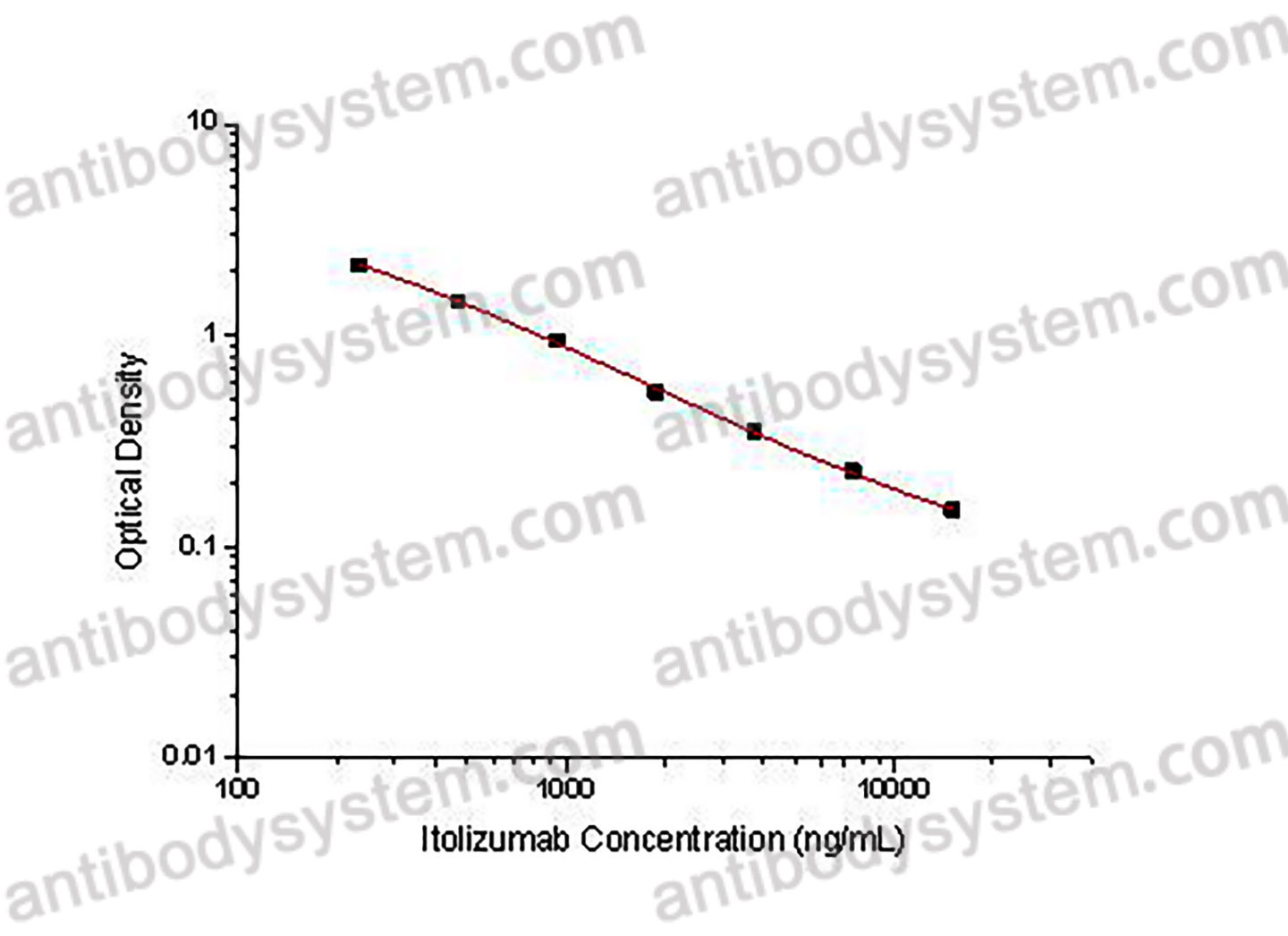
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human CD6 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Itolizumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Itolizumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Itolizumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Itolizumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
234.38 - 15,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
69.97 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
8602.7
|
2108.8
|
479.2
|
7870.5
|
1833.1
|
447.7
|
|
Standard deviation
|
1032.7
|
200.3
|
63.1
|
1410.1
|
227.1
|
82.3
|
|
CV (%)
|
12.0
|
9.5
|
13.2
|
17.9
|
12.4
|
18.4
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
T1h, CAS: 1116433-11-4
Background
Itolizumab, a humanized anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, is a new molecule that acts by immunomodulating the CD6 molecule. CD6 is a co-stimulatory molecule required for optimal T-cell stimulation by the antigen-presenting cells. This step is crucial in T-cell proliferation to form Th1 and Th17 cells, which play a major role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Itolizumab regulates activating and inhibitory signals on effector cells, improving their cytotoxicity against CD318+ tumor cell lines., PMID:40391211
Corrigendum to: Comparative evaluation of tocilizumab and itolizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in India: a retrospective cohort study., PMID:39622603
Contemporary Updates in the Prevention and Treatment of Graft-Versus-Host Disease., PMID:39520614
Long-term therapy with itolizumab is safe and effective for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from an expanded-access program., PMID:38759368
Comparative evaluation of tocilizumab and itolizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in India: a retrospective cohort study., PMID:38556909
Role of Itolizumab in the Treatment of COVID-19 Patients, Admitted to ICU at a Tertiary Care Hospital., PMID:37355865
REcovery and SURvival of patients with moderate to severe acute REspiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to COVID-19: a multicenter, single-arm, Phase IV itolizumab Trial: RESURRECT., PMID:37073744
Anti CD-6 Monoclonal Antibodies in the Management of Generalised Pustular Psoriasis., PMID:36865872
Adverse drug reactions of itolizumab in COVID-19 patient: A case report., PMID:36537408
Severe bronchospasm following itolizumab infusion in a COVID-19 patient., PMID:36060191
COVID-19 mortality and its predictors in the elderly: A systematic review., PMID:35620541
Phenotypic and functional characterization of the CD6-ALCAM T-cell co-stimulatory pathway after allogeneic cell transplantation., PMID:35484649
An Exploratory Study of Itolizumab on the Preservation of Beta Cell Function in Adults with Recent-Onset Type 1 Diabetes., PMID:35407396
Pharmacological treatment of COVID-19: an opinion paper., PMID:34894208
Cytokine Storm and Immunomodulation in COVID-19., PMID:34866828
Potential effects of itolizumab treatment on plasma interleukin-6 levels in patients with severe COVID-19., PMID:34169913
Second-degree Heart Block Caused by Itolizumab-induced Infusion Reaction in COVID-19., PMID:34045820
Off-label Use of Itolizumab in Patients with COVID-19 ARDS: Our Clinical Experience in a Dedicated COVID Center., PMID:34045817
Monoclonal Antibodies vs COVID-19: Eduardo Ojito-Magaz MS General Director, Molecular Immunology Center., PMID:33974610
A two-arm, randomized, controlled, multi-centric, open-label phase-2 study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Itolizumab in moderate to severe ARDS patients due to COVID-19., PMID:33835886
Itolizumab Treatment for Cytokine Release Syndrome in Moderate to Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Due to COVID-19: Clinical Outcomes, A Retrospective Study., PMID:33527804
Antibodies to watch in 2021., PMID:33459118
An anti-CD6 antibody for the treatment of COVID-19 patients with cytokine-release syndrome: report of three cases., PMID:33397150
Pulmonary Thrombosis in COVID-19 Treated by Thrombolysis: A Small Case Series Using Streptokinase., PMID:33378782
Comparative efficacy and safety of pharmacological interventions for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis., PMID:33378357
Possible treatment and strategies for COVID-19: review and assessment., PMID:33336780
Treatment of COVID-19 patients with the anti-CD6 antibody itolizumab., PMID:33304584
An anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody (itolizumab) reduces circulating IL-6 in severe COVID-19 elderly patients., PMID:33292350
Scientists criticize use of unproven COVID drugs in India., PMID:33169025
Use of a Humanized Anti-CD6 Monoclonal Antibody (Itolizumab) in Elderly Patients with Moderate COVID-19., PMID:33105142
Immune Therapy, or Antiviral Therapy, or Both for COVID-19: A Systematic Review., PMID:33068263
Approval of Itolizumab for COVID-19: A Premature Decision or Need of The Hour?, PMID:33048300
Are We Jumping the Gun with Itolizumab in India? A Situational Analysis from the Pre-COVID Era., PMID:33015549
Itolizumab, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, as a potential treatment for COVID-19 complications., PMID:32700604
Anti-CD6 mAbs for the treatment of psoriasis., PMID:32466689
A retrospective case series of 12 patients with chronic reactive arthritis with emphasis on treatment outcome with biologics., PMID:31293276
Spotlight on itolizumab in the treatment of psoriasis - current perspectives from India., PMID:31119094
New Targeted Therapies for Uncontrolled Asthma., PMID:31076057
Comparative efficacy and safety of thirteen biologic therapies for patients with moderate or severe psoriasis: A network meta-analysis., PMID:30922656
CD6 monoclonal antibodies differ in epitope, kinetics and mechanism of action., PMID:29772075
Clinical and experimental evidence for targeting CD6 in immune-based disorders., PMID:29526637
Correction: T cell activation and differentiation is modulated by a CD6 domain 1 antibody Itolizumab., PMID:29381749
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis., PMID:29271481
Commentary: CD6 As a Potential Target for Treating Multiple Sclerosis., PMID:29033937
Itolizumab - A New Biologic for Management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis., PMID:29033818
The anti-CD6 antibody itolizumab provides clinical benefit without lymphopenia in rheumatoid arthritis patients: results from a 6-month, open-label Phase I clinical trial., PMID:28963724
Itolizumab in the Management of Psoriasis with Metabolic Syndrome., PMID:28893023
Itolizumab in Psoriasis., PMID:28794555
A Real-World Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Itolizumab in Patients with Chronic Plaque Psoriasis., PMID:28761839
T cell activation and differentiation is modulated by a CD6 domain 1 antibody Itolizumab., PMID:28672038