Catalog No.
KDB95903
Description
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human CD4 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Zanolimumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Zanolimumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Zanolimumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
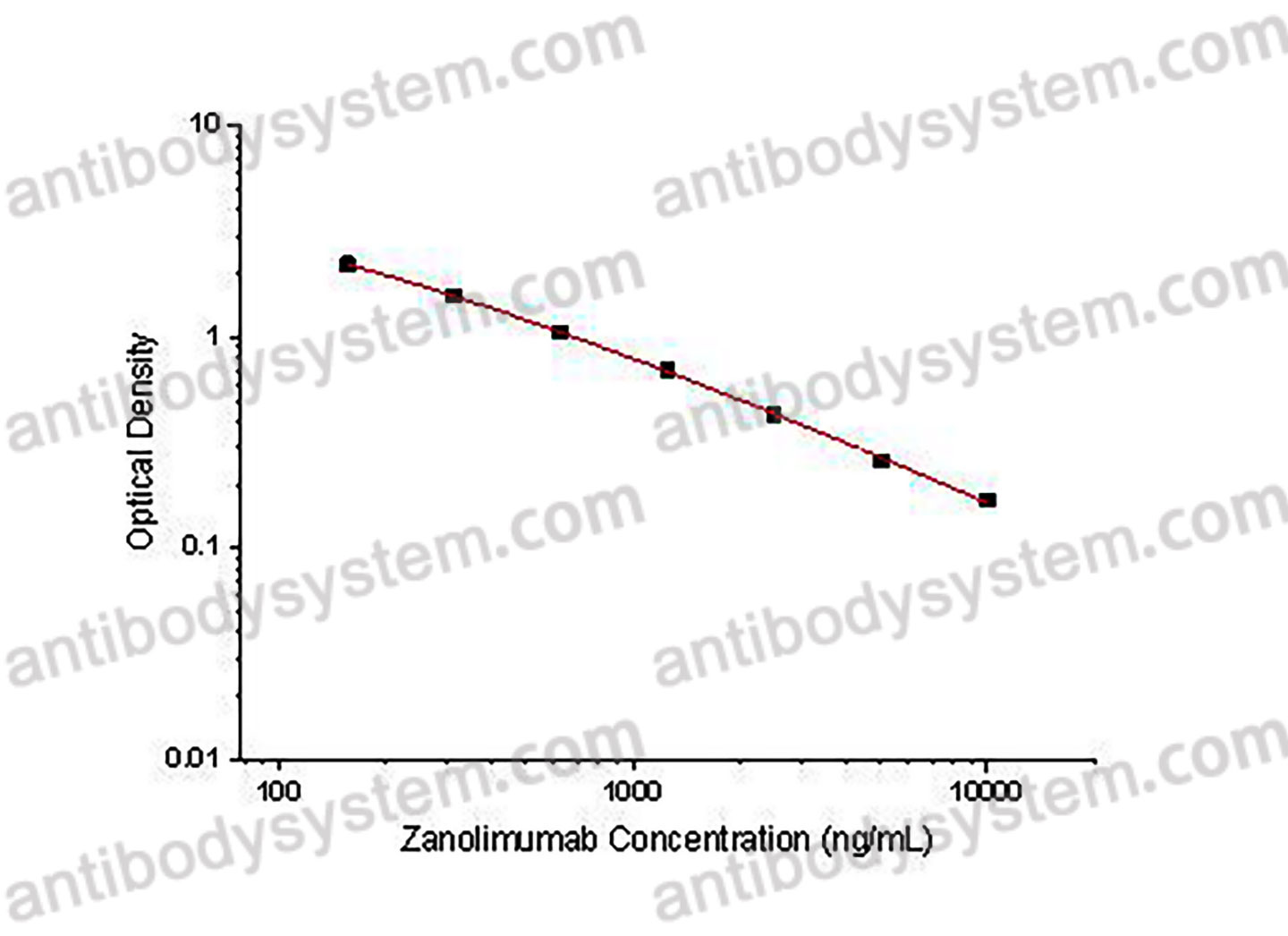
Used for the quantitative determination of Zanolimumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
156.25 - 10,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
80.12 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision |
Inter-Assay Precision |
||||
|
Sample |
1 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
n |
16 |
16 |
16 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
|
Mean (ng/mL) |
6426.4 |
1304.6 |
330.4 |
5624.2 |
1380.2 |
292.4 |
|
Standard deviation |
774.4 |
150.5 |
37.7 |
463.8 |
138.1 |
34.4 |
|
CV (%) |
12.1 |
11.5 |
11.4 |
8.2 |
10.0 |
11.8 |
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
HuMax-CD4, CAS: 652153-01-0
Background
Zanolimumab is a biosimilar that targets CD4. The CD4 antigen is involved in the recognition of MHC class II molecules and is a co-receptor for HIV. CD4 is primarily expressed in a subset of T-lymphocytes, also referred to as T helper cells, but may also be expressed by other cells in the immune system, such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. At the tissue level, CD4 expression may be detected in thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen, and also in specific regions of the brain, gut, and other non-lymphoid tissues. CD4 functions to initiate or augment the early phase of T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase, Lck. It may also function as an important mediator of direct neuronal damage in infectious and immune-mediated diseases of the central nervous system. Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts have been identified in this gene [RefSeq, July 2017].