Catalog No.
KDB95901
Description
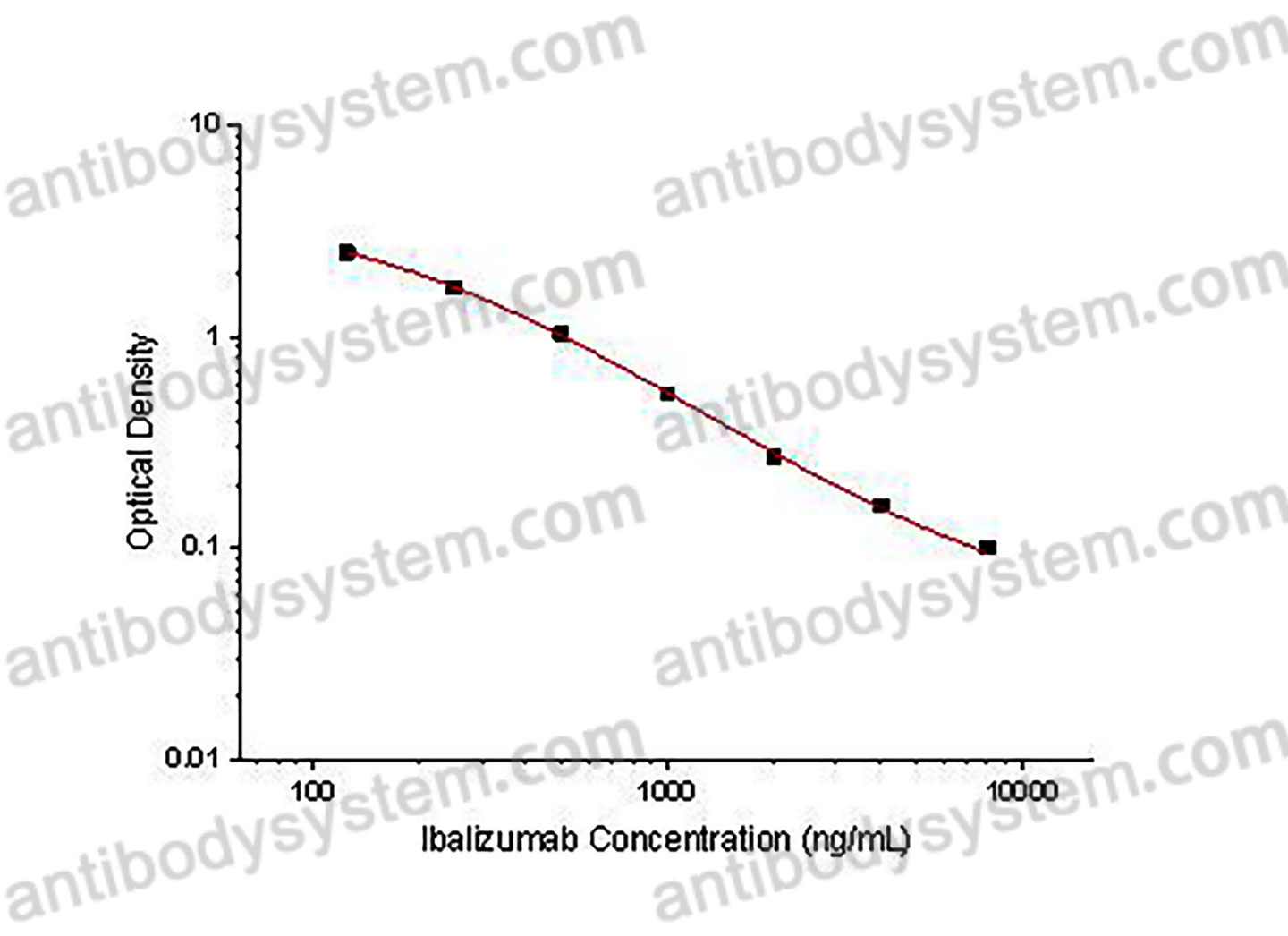
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human CD4 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Ibalizumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Ibalizumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Ibalizumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Ibalizumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
125 - 8,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
64.71 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
4179.9
|
986.7
|
225.1
|
4606.6
|
1239.3
|
280.7
|
|
Standard deviation
|
216.3
|
51.6
|
25.4
|
511.3
|
178.4
|
33.0
|
|
CV (%)
|
5.2
|
5.2
|
11.3
|
11.1
|
14.4
|
11.7
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
The stability of ELISA kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 10% prior to the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Alternative Names
Hu5A8, TMB-355, TNX-355, CAS: 680188-33-4
Background
Ibalizumab, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody, represents the first novel agent for HIV-1 management in over a decade and is the first monoclonal antibody for the treatment of MDR HIV-1 infection in combination with other forms of antiretroviral therapy in heavily treatment-experienced adults who are failing their current antiretroviral regimen. Ibalizumab demonstrates a novel mechanism of action as a CD4-directed postattachment inhibitor and has a favorable pharmacokinetic profile that allows for a dosing interval of every 14 days after an initial loading dose. Clinical studies have demonstrated reasonably substantial antiretroviral activity with ibalizumab among a complex patient population with advanced HIV-1 infection who are receiving an optimized background regimen, where limited therapeutic options exist. Ibalizumab was well tolerated in clinical trials, and the most common adverse effects included diarrhea, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, pyrexia, and rash. Resistance to ibalizumab has also been observed via reduced expression or loss of the potential N-linked glycosylation sites in the V5 loop of the envelope glycoprotein 120. The mechanism of action, pharmacokinetic parameters, efficacy, and safety of ibalizumab present an advance in the management of MDR HIV-1 infection. Future studies and postmarketing experience will further determine longer-term clinical efficacy, safety, and resistance data for ibalizumab.
Ibalizumab plus an optimized background regimen in treatment-experienced patients infected with multidrug resistant HIV-1: A phase 3, multicenter, expanded access study., PMID:40465394
FlowDesign: Improved design of antibody CDRs through flow matching and better prior distributions., PMID:40306278
Investigating the combination of Temsavir and entry inhibitors on HIV replication: Synergistic and antagonistic effects observed against various R5-tropic envelopes., PMID:39642611
PRESTIGIO RING: "A 28-year-old highly treatmentexperienced man with vertical HIV infection on ibalizumab therapy: ART simplification perspectives"., PMID:39560045
Emerging integrase resistance in an international perinatal virtual clinic., PMID:39469738
Expanding Treatment Opportunities: Reviewing the Current State of Injectable Antiretrovirals for Treatment of HIV., PMID:39417932
Efficacy and Safety of 2 Fixed Doses of Ibalizumab Plus Optimized Background Regimen in Treatment-Experienced HIV-Positive Individuals., PMID:39250331
US cost-utility model of lenacapavir plus optimized background regimen (OBR) vs fostemsavir plus OBR and ibalizumab plus OBR for people with HIV with multidrug resistance., PMID:39213144
A Narrative Review of Novel Agents for Managing Heavily Treatment-Experienced People Living With HIV., PMID:39157636
Highly potent and broadly neutralizing anti-CD4 trimeric nanobodies inhibit HIV-1 infection by inducing CD4 conformational alteration., PMID:39138183
Strategic use of salvage long-acting antiretrovirals in the setting of resistance., PMID:39045845
Consensus recommendations for use of long-acting antiretroviral medications in the treatment and prevention of HIV-1: Endorsed by the American Academy of HIV Medicine, American College of Clinical Pharmacy, Canadian HIV and Viral Hepatitis Pharmacists Network, European AIDS Clinical Society, and Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists: An executive summary., PMID:39005161
Consensus recommendations for use of long-acting antiretroviral medications in the treatment and prevention of HIV-1: Endorsed by the American Academy of HIV Medicine, American College of Clinical Pharmacy, Canadian HIV and Viral Hepatitis Pharmacists Network, European AIDS Clinical Society, and Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists., PMID:39005160
Characterization of clinical envelopes with lack of sensitivity to the HIV-1 inhibitors temsavir and ibalizumab., PMID:38971430
Consensus recommendations for the use of novel antiretrovirals in persons with HIV who are heavily treatment-experienced and/or have multidrug-resistant HIV-1: Endorsed by the American Academy of HIV Medicine, American College of Clinical Pharmacy: An executive summary., PMID:38853605
Consensus recommendations for the use of novel antiretrovirals in persons with HIV who are heavily treatment-experienced and/or have multidrug-resistant HIV-1: Endorsed by the American Academy of HIV Medicine, American College of Clinical Pharmacy., PMID:38853601
Ex vivo sensitivity to broadly neutralizing antibodies and anti-CD4 antibody UB-421 of infectious viral isolates from people living with multidrug-resistant HIV., PMID:38728839
Salvage Therapy Including Foscarnet and Ibalizumab for Multidrug-Resistant Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2 Infection., PMID:38630945
Cross-resistance to entry inhibitors and lenacapavir resistance through Week 52 in study CAPELLA., PMID:38085652
Identification of potential therapeutic drugs targeting core genes for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and coexisting COVID-19: Insights from bioinformatic analyses., PMID:38018597
Pharmacokinetics of Antiretroviral Drugs in Older People Living with HIV: A Systematic Review., PMID:37561283
Efficacy and Safety of Two-Drug Regimens That Are Approved from 2018 to 2022 for the Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Disease and Its Opportunistic Infections., PMID:37374953
Lenacapavir (Sunlenca) for multidrug-resistant HIV., PMID:37155250
Indirect Treatment Comparisons of Lenacapavir Plus Optimized Background Regimen Versus Other Treatments for Multidrug-Resistant Human Immunodeficiency Virus., PMID:36566886
Realizing the promise of long-acting antiretroviral treatment strategies for individuals with HIV and adherence challenges: an illustrative case series., PMID:36435793
HIV-1 bispecific antibody iMab-N6 exhibits enhanced breadth but not potency over its parental antibodies iMab and N6., PMID:36071449
Quantitative PET imaging of the CD4 pool in nonhuman primates., PMID:36028577
Design of a Bispecific HIV Entry Inhibitor Targeting the Cell Receptor CD4 and Viral Fusion Protein Gp41., PMID:35711654
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Fostemsavir in Heavily Treatment-Experienced People With HIV-1., PMID:35610081
Covalent binding of human two-domain CD4 to an HIV-1 subtype C SOSIP.664 trimer modulates its structural dynamics., PMID:35550505
Ibalizumab shows in-vitro activity against group A and group B HIV-2 clinical isolates., PMID:35262531
Achieving virological control in pan-resistant HIV-1 infection: A case series., PMID:35255457
Novel Bent Conformation of CD4 Induced by HIV-1 Inhibitor Indirectly Prevents Productive Viral Attachment., PMID:34896364
Clinical evidence for a lack of cross-resistance between temsavir and ibalizumab or maraviroc., PMID:34628442
Reactivation of Hepatitis B After Ibalizumab Therapy for Multidrug-Resistant Human Immunodeficiency Virus., PMID:34549064
Hepatotoxicity of contemporary antiretroviral drugs., PMID:34545037
Broad and potent bispecific neutralizing antibody gene delivery using adeno-associated viral vectors for passive immunization against HIV-1., PMID:34509584
Ibalizumab-uiyk as a bridge therapy for a patient with drug-resistant HIV-1 infection receiving chemotherapy: A case report., PMID:34111306
The Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Impact of Ibalizumab-uiyk for Adults with Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 Infection in the United States., PMID:33532919
Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics, and Safety Over 48 Weeks With Ibalizumab-Based Therapy in Treatment-Experienced Adults Infected With HIV-1: A Phase 2a Study., PMID:33427765
Cerebrospinal fluid viral replication and burden of resistance in three HIV-1-infected people taking Ibalizumab with multiple drug class-wide resistance., PMID:33105172
Cancer immunotherapy via targeted TGF-β signalling blockade in TH cells., PMID:33087933
Cross-species/cross-modality physiologically based pharmacokinetics for biologics: 89Zr-labelled albumin-binding domain antibody GSK3128349 in humans., PMID:33073698
Antibody-based strategies in HIV therapy., PMID:33045349
Ibalizumab: The First Monoclonal Antibody for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection., PMID:32659101
Monoclonal Antibodies Against Infectious Microbes: So Long and Too Little!, PMID:32164518
Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies: An Update., PMID:32152957
Ibalizumab: A Review in Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 Infection., PMID:31970712
Clinical and Economic Impact of Ibalizumab for People With Multidrug-Resistant HIV in the United States., PMID:31929403