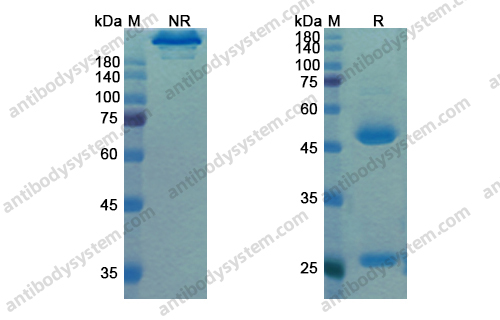
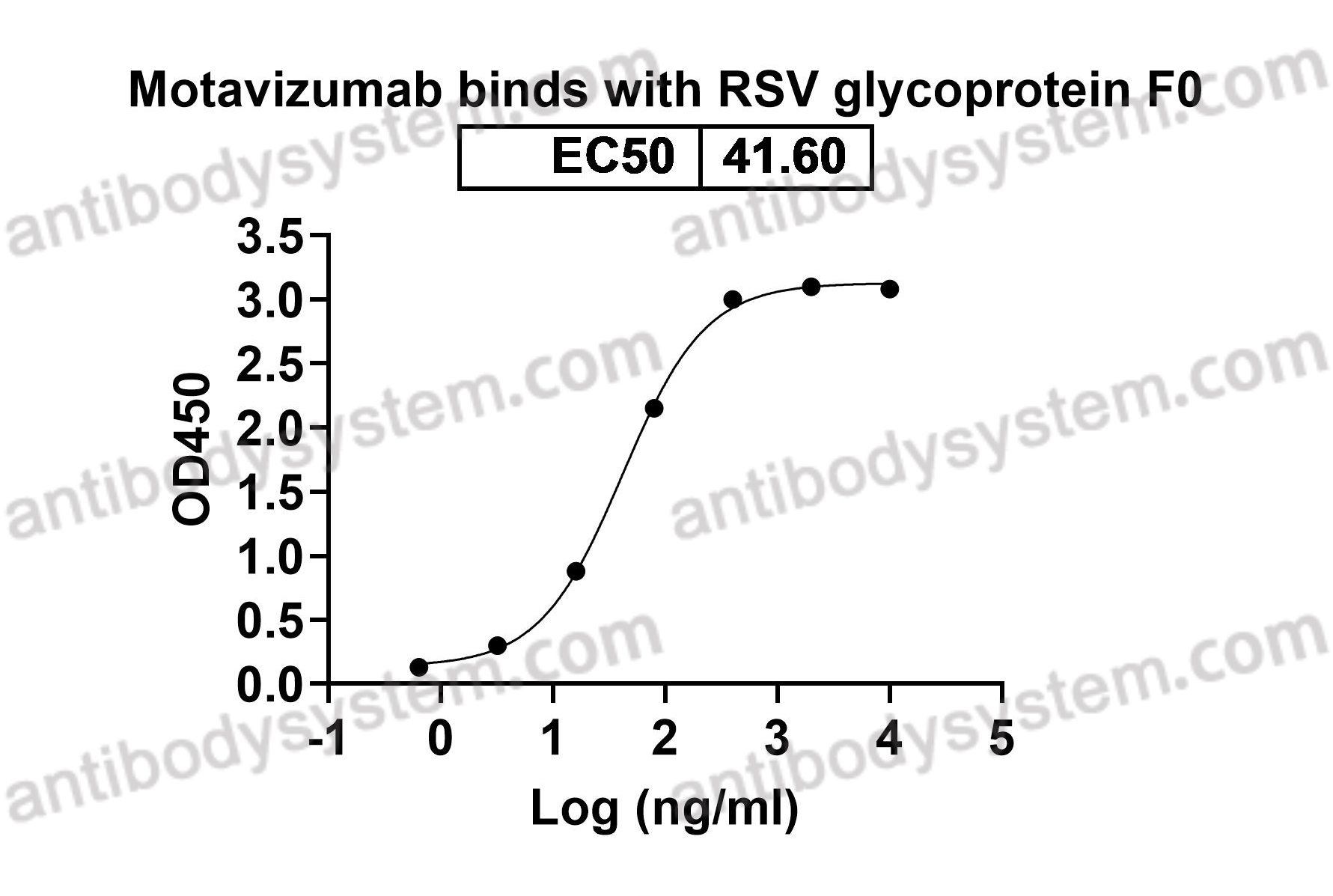
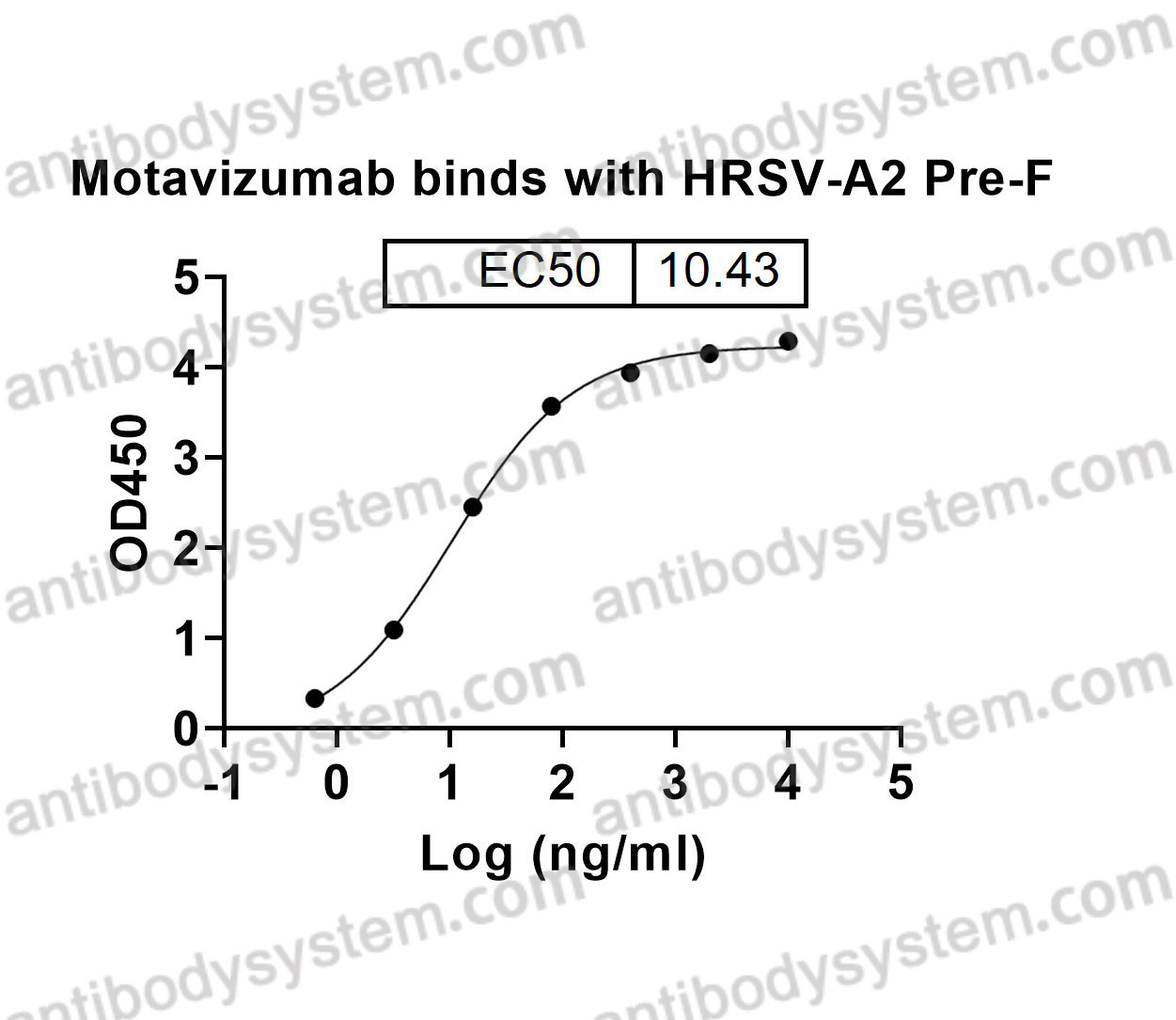
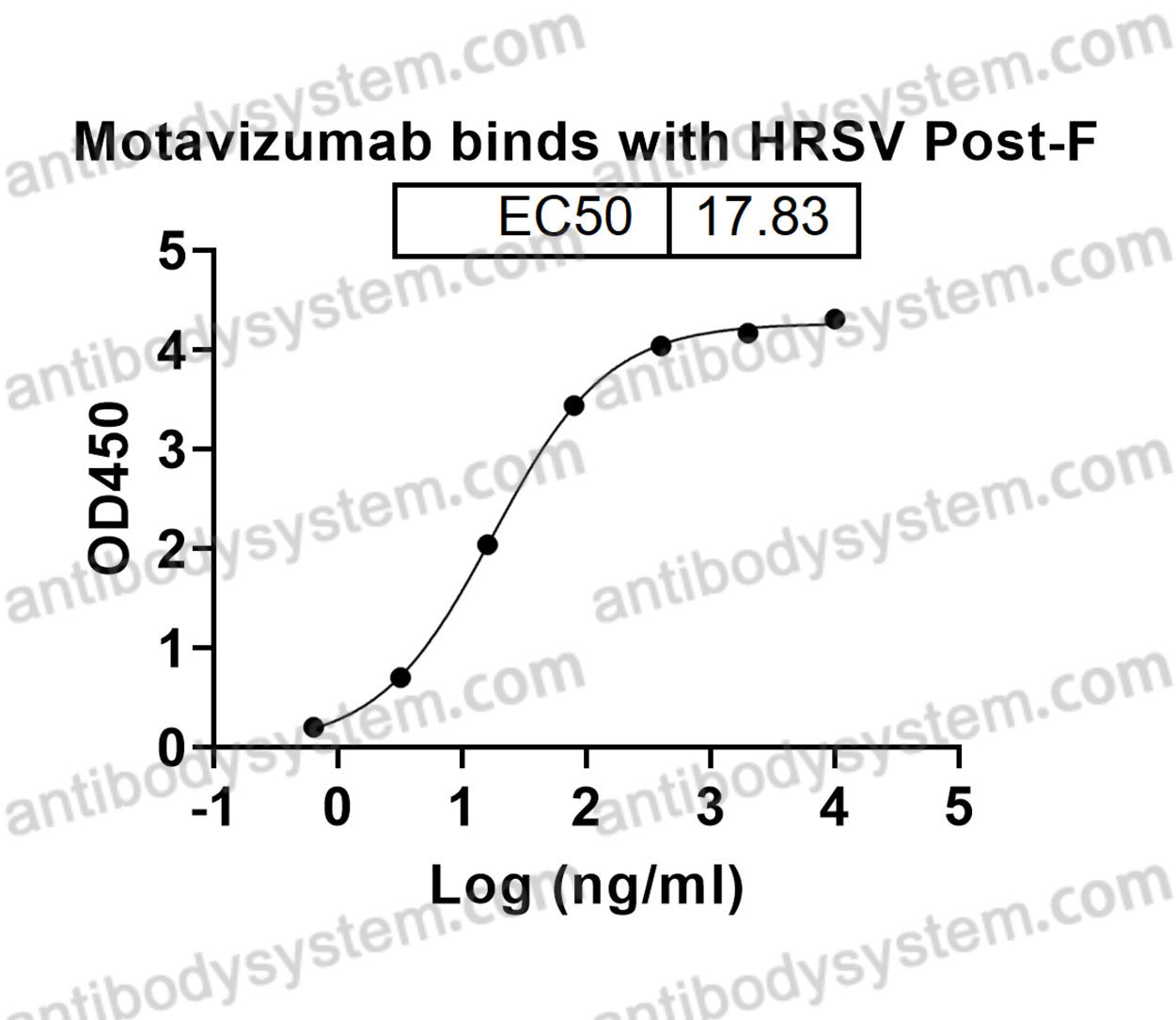
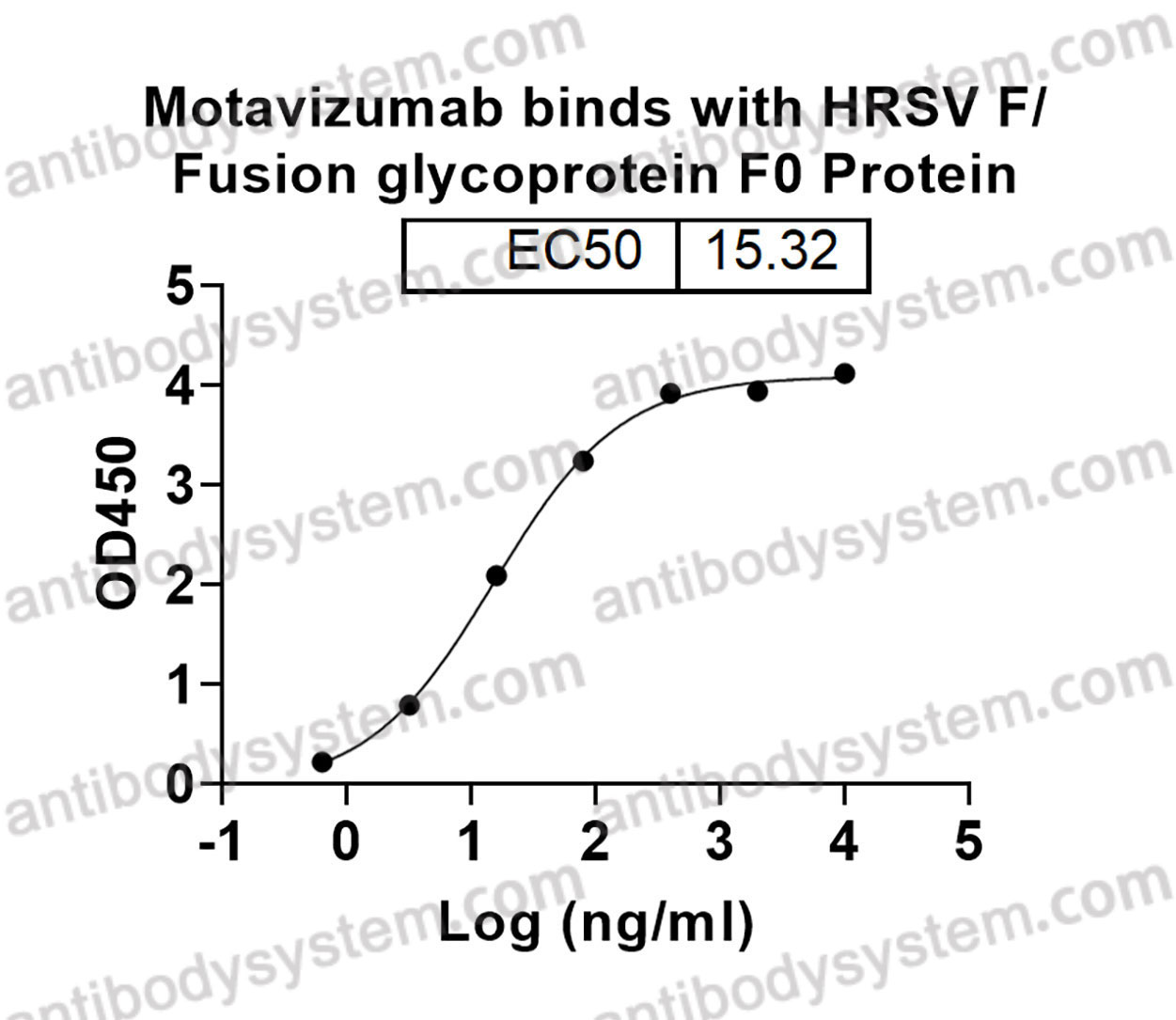
Motavizumab, PMID: 20065632
Motavizumab for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants, PMID: 19764889
Motavizumab, RSV, and subsequent wheezing, PMID: 27301921
Motavizumab, RSV, and subsequent wheezing - Authors' reply, PMID: 27998592
Motavizumab for prophylaxis of respiratory syncytial virus in high-risk children: a noninferiority trial, PMID: 20008423
Reformatting palivizumab and motavizumab from IgG to human IgA impairs their efficacy against RSV infection in vitro and in vivo, PMID: 29553863
Motavizumab treatment of infants hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus infection does not decrease viral load or severity of illness, PMID: 24356256
Motavizumab, a second-generation humanized mAb for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk populations, PMID: 19330726
Motavizumab, a neutralizing anti-Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Rsv) monoclonal antibody significantly modifies the local and systemic cytokine responses induced by Rsv in the mouse model, PMID: 17961258
Immunoprophylaxis of RSV infection: advancing from RSV-IGIV to palivizumab and motavizumab, PMID: 17990791
Efficacy of motavizumab for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus disease in healthy Native American infants: a phase 3 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial, PMID: 26511956
Respiratory syncytial virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies motavizumab and palivizumab inhibit fusion, PMID: 20519399
A novel investigational Fc-modified humanized monoclonal antibody, motavizumab-YTE, has an extended half-life in healthy adults, PMID: 24080653
A randomized controlled trial of motavizumab versus palivizumab for the prophylaxis of serious respiratory syncytial virus disease in children with hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, PMID: 21522037
Properties of human IgG1s engineered for enhanced binding to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), PMID: 16793771
Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of motavizumab, a humanized, enhanced-potency monoclonal antibody for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in at-risk children, PMID: 19258920
Product review on the monoclonal antibody palivizumab for prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection, PMID: 28605249
Structural basis of respiratory syncytial virus neutralization by motavizumab, PMID: 20098425
Design and characterization of epitope-scaffold immunogens that present the motavizumab epitope from respiratory syncytial virus, PMID: 21549714
A phase 2, randomized, double-blind safety and pharmacokinetic assessment of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prophylaxis with motavizumab and palivizumab administered in the same season, PMID: 20525274
Safety and antiviral activity of motavizumab, a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-specific humanized monoclonal antibody, when administered to RSV-infected children, PMID: 19636278
Development of motavizumab, an ultra-potent antibody for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in the upper and lower respiratory tract, PMID: 17362988
Updated guidance for palivizumab prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection, PMID: 25070304
Analysis of respiratory syncytial virus preclinical and clinical variants resistant to neutralization by monoclonal antibodies palivizumab and/or motavizumab, PMID: 21208913
Computational redesign of human respiratory syncytial virus epitope as therapeutic peptide vaccines against pediatric pneumonia, PMID: 29500665
Evaluation of a synthetic peptide as a replacement for the recombinant fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus in a potency ELISA, PMID: 20943340
Pharmacological management of human respiratory syncytial virus infection, PMID: 32808830
Structure of respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein in the postfusion conformation reveals preservation of neutralizing epitopes, PMID: 21613394
[Anti RS virus drugs], PMID: 22568137
The long road to protect infants against severe RSV lower respiratory tract illness, PMID: 31105933
A review of palivizumab and emerging therapies for respiratory syncytial virus, PMID: 21831008
In silico approach towards designing virtual oligopeptides for HRSV, PMID: 25525622
Cost effectiveness of respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis: a critical and systematic review, PMID: 20131925
Respiratory syncytial virus disease: update on treatment and prevention, PMID: 21171875
Letter from the editor, PMID: 20065631
An epitope-specific chemically defined nanoparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus, PMID: 34145291
Evolution of prophylaxis: MoAb, siRNA, vaccine, and small molecules, PMID: 19651397
Prospects for the development of fusion inhibitors to treat human respiratory syncytial virus infection, PMID: 19562644
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prevention and treatment: past, present, and future, PMID: 19689261
New strategies for control of respiratory syncytial virus infection, PMID: 18978532
Prophylaxis and treatment of respiratory syncytial virus in adult immunocompromised patients, PMID: 22395247
Monoclonal antibody for reducing the risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children, PMID: 23633336
Boosting subdominant neutralizing antibody responses with a computationally designed epitope-focused immunogen, PMID: 30789898
Past, Present and Future Approaches to the Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children, PMID: 29470837
Adeno-Associated Virus Vector-Mediated Expression of Antirespiratory Syncytial Virus Antibody Prevents Infection in Mouse Airways, PMID: 34415793
A Minimal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model with a Nested Endosome Compartment for Novel Engineered Antibodies, PMID: 29541870
An Epitope-Specific Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Based on an Antibody Scaffold, PMID: 26434555
Induction of high titred, non-neutralising antibodies by self-adjuvanting peptide epitopes derived from the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein, PMID: 28894111
Characterization of neutralizing affinity-matured human respiratory syncytial virus F binding antibodies in the sub-picomolar affinity range, PMID: 22407977
Respiratory syncytial virus: diagnosis, treatment and prevention, PMID: 23055894
Impact of RSV Prevention in Infancy on Prevalence of Asthma Among 9-14-Year-old Native American Children in the Southwest United States., PMID:40208934
The Cumulative Variations of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein (F) in Ten Consecutive Years in China., PMID:39452166
Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination and Receipt of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Antibody (Nirsevimab) by Infants Aged <8 Months - United States, April 2024., PMID:39325675
[Nirsevimab effectiveness against hospital admission for respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infants]., PMID:39308353
Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Safety of RSV-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies and Antivirals in Development., PMID:39209729
Cost-effectiveness of RSVpreF vaccine and nirsevimab for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus disease in Canadian infants., PMID:39079810
Effectiveness of nirsevimab introduction against respiratory syncytial virus in the Valencian Community: A preliminary assessment., PMID:38834430
Immunogenicity of a recombinant plant-produced respiratory syncytial virus F subunit vaccine in mice., PMID:38234330
Inhaled "Muco-Trapping" Monoclonal Antibody Effectively Treats Established Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infections., PMID:38225749
Immunoglobulin treatment for hospitalised infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection., PMID:37870128
Immunoinformatics aided approach for predicting potent cytotoxic T cell epitopes of respiratory syncytial virus., PMID:36935101
Monoclonal Antibody for the Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis., PMID:36800182
Backbone and side-chain resonance assignments of the NISTmAb-scFv and antigen-binding study., PMID:36083574
Molecular Modeling Predicts Novel Antibody Escape Mutations in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Glycoprotein., PMID:35678603
Adeno-Associated Virus Vector-Mediated Expression of Antirespiratory Syncytial Virus Antibody Prevents Infection in Mouse Airways., PMID:34415793
An epitope-specific chemically defined nanoparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus., PMID:34145291
Pharmacological management of human respiratory syncytial virus infection., PMID:32808830
A Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model for the Prediction of "Half-Life Extension" and "Catch and Release" Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics., PMID:32697437
Immunoglobulin treatment for hospitalised infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection., PMID:31446622
The long road to protect infants against severe RSV lower respiratory tract illness., PMID:31105933
Boosting subdominant neutralizing antibody responses with a computationally designed epitope-focused immunogen., PMID:30789898
Reformatting palivizumab and motavizumab from IgG to human IgA impairs their efficacy against RSV infection in vitro and in vivo., PMID:29553863
A Minimal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model with a Nested Endosome Compartment for Novel Engineered Antibodies., PMID:29541870
Computational redesign of human respiratory syncytial virus epitope as therapeutic peptide vaccines against pediatric pneumonia., PMID:29500665
Past, Present and Future Approaches to the Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children., PMID:29470837
Two-Pore Minimum Physiologically-based Pharmacokinetic Model to Describe the Disposition of Therapeutic Monoclonal IgG Antibody in Humans., PMID:29411151
The Heptad Repeat C Domain of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein Plays a Key Role in Membrane Fusion., PMID:29212939
Induction of high titred, non-neutralising antibodies by self-adjuvanting peptide epitopes derived from the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein., PMID:28894111
Product review on the monoclonal antibody palivizumab for prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection., PMID:28605249
Motavizumab, RSV, and subsequent wheezing - Authors' reply., PMID:27998592
Structural basis for nonneutralizing antibody competition at antigenic site II of the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein., PMID:27791117
Motavizumab, RSV, and subsequent wheezing., PMID:27301921
Development of Electrochemiluminescent Serology Assays to Measure the Humoral Response to Antigens of Respiratory Syncytial Virus., PMID:27070145
Efficacy of motavizumab for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus disease in healthy Native American infants: a phase 3 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial., PMID:26511956
An Epitope-Specific Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Based on an Antibody Scaffold., PMID:26434555
In silico approach towards designing virtual oligopeptides for HRSV., PMID:25525622
An insect cell derived respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) F nanoparticle vaccine induces antigenic site II antibodies and protects against RSV challenge in cotton rats by active and passive immunization., PMID:25269094
Updated guidance for palivizumab prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection., PMID:25070304
Escape from neutralization by the respiratory syncytial virus-specific neutralizing monoclonal antibody palivizumab is driven by changes in on-rate of binding to the fusion protein., PMID:24725940
Motavizumab treatment of infants hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus infection does not decrease viral load or severity of illness., PMID:24356256
A novel investigational Fc-modified humanized monoclonal antibody, motavizumab-YTE, has an extended half-life in healthy adults., PMID:24080653
Monoclonal antibody for reducing the risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children., PMID:23633336
[Anti RS virus drugs]., PMID:22568137
Testing superiority at interim analyses in a non-inferiority trial., PMID:22438208
Characterization of neutralizing affinity-matured human respiratory syncytial virus F binding antibodies in the sub-picomolar affinity range., PMID:22407977
Prophylaxis and treatment of respiratory syncytial virus in adult immunocompromised patients., PMID:22395247
Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus infection in preterm infants., PMID:22262986
A review of palivizumab and emerging therapies for respiratory syncytial virus., PMID:21831008
Structure of respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein in the postfusion conformation reveals preservation of neutralizing epitopes., PMID:21613394
Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers., PMID:21586636