Catalog No.
YHG38501
Expression system
E. coli
Species
Homo sapiens (Human)
Protein length
Pro101-Ile366
Predicted molecular weight
31.89 kDa
Nature
Recombinant
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
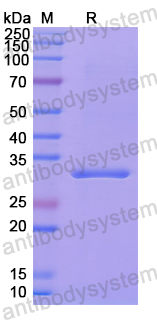
Purity
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Accession
Q13057
Applications
ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Form
Lyophilized
Storage buffer
Lyophilized from a solution in PBS pH 7.4, 0.02% NLS, 1mM EDTA, 4% Trehalose, 1% Mannitol.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute in sterile water for a stock solution. A copy of datasheet will be provided with the products, please refer to it for details.
Shipping
In general, proteins are provided as lyophilized powder/frozen liquid. They are shipped out with dry ice/blue ice unless customers require otherwise.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Alternative Names
Bifunctional coenzyme A synthase, PPAT, NBP, Dephospho-CoA pyrophosphorylase, Dephosphocoenzyme A kinase, DPCK, COASY, POV-2, CoA synthase, Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase, DPCOAK
The role and machine learning analysis of mitochondrial autophagy-related gene expression in lung adenocarcinoma., PMID:40313958
Fibroblasts and hiPS-Derived Astrocytes From CoPAN Patients Showed Different Levels of Iron Overload Correlated With Senescent Phenotype., PMID:40105046
Impaired mitochondrial integrity and compromised energy production underscore the mechanism underlying CoASY protein-associated neurodegeneration., PMID:39985665
Metabolic alterations in fibroblasts of patients presenting with the MPAN subtype of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA)., PMID:39419454
CoA synthase plays a critical role in neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration., PMID:39301217
Emerging variants, unique phenotypes, and transcriptomic signatures: an integrated study of COASY-associated diseases., PMID:38750253
COASY Protein-Associated Neurodegeneration: Report from India., PMID:38022473
Brain CoA and Acetyl CoA Metabolism in Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration., PMID:37080933
Predictive biomarkers in radioresistant rectal cancer: A systematic review., PMID:37059272
Inherited Disorders of Coenzyme A Biosynthesis: Models, Mechanisms, and Treatments., PMID:36983025
Vitamin B5 and succinyl-CoA improve ineffective erythropoiesis in SF3B1-mutated myelodysplasia., PMID:36857430
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: a case series highlighting phenotypic and genotypic diversity in 20 Indian families., PMID:36790591
Pathogenic variants of the coenzyme A biosynthesis-associated enzyme phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase cause autosomal-recessive dilated cardiomyopathy., PMID:36564894
Progressive brain atrophy and severe neurodevelopmental phenotype in siblings with biallelic COASY variants., PMID:36495139
The transcription factor c-Jun inhibits RBM39 to reprogram pre-mRNA splicing during genotoxic stress., PMID:36477312
VP26, a herpes simplex virus type 1 capsid protein, increases DNA methylation in COASY promoter region., PMID:36345321
COASY related pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 12: A common Indian mutation with expansion of the phenotypic spectrum., PMID:35499143
Identification of Novel Key Molecular Signatures in the Pathogenesis of Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease., PMID:35432190
Lifetime risk of autosomal recessive neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) disorders calculated from genetic databases., PMID:35180557
Coenzyme a Biochemistry: From Neurodevelopment to Neurodegeneration., PMID:34439650
Consensus clinical management guideline for beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration., PMID:34347296
Recent Evidence in Epigenomics and Proteomics Biomarkers for Early and Minimally Invasive Diagnosis of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases., PMID:33357195
Neuronal Ablation of CoA Synthase Causes Motor Deficits, Iron Dyshomeostasis, and Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in a CoPAN Mouse Model., PMID:33352696
Footprinting SHAPE-eCLIP Reveals Transcriptome-wide Hydrogen Bonds at RNA-Protein Interfaces., PMID:33242392
CoAsy knockdown in TNBC cell lines resulted in no overt effect on cell proliferation in vitro., PMID:32828275
Increased blood COASY DNA methylation levels a potential biomarker for early pathology of Alzheimer's disease., PMID:32699290
CoA Synthase (COASY) Mediates Radiation Resistance via PI3K Signaling in Rectal Cancer., PMID:31704889
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: Insights into the mitochondria dysregulation., PMID:31404774
Silencing of pantothenate kinase 2 reduces endothelial cell angiogenesis., PMID:30221726
Overexpression of Human Mutant PANK2 Proteins Affects Development and Motor Behavior of Zebrafish Embryos., PMID:30141000
Biallelic loss of function variants in COASY cause prenatal onset pontocerebellar hypoplasia, microcephaly, and arthrogryposis., PMID:30089828
Integrated Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology Approach to Explain Possible Action Mechanisms of Xin-Sheng-Hua Granule for Treating Anemia., PMID:29551975
CoA synthase regulates mitotic fidelity via CBP-mediated acetylation., PMID:29531224
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation., PMID:29325618
Novel mutations in PANK2 and PLA2G6 genes in patients with neurodegenerative disorders: two case reports., PMID:28821231
Diagnosis of CoPAN by whole exome sequencing: Waking up a sleeping tiger's eye., PMID:28489334
Usefulness of DNA Methylation Levels in COASY and SPINT1 Gene Promoter Regions as Biomarkers in Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment., PMID:27992572
Down-regulation of coasy, the gene associated with NBIA-VI, reduces Bmp signaling, perturbs dorso-ventral patterning and alters neuronal development in zebrafish., PMID:27892483
[GENETICALLY DETERMINED DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH PATHOLOGICAL BRAIN IRON ACCUMULATION AND NEURODEGENERATION]., PMID:27468605
Mutational analysis of COASY in an Italian patient with NBIA., PMID:27021474
High frequency of beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration (BPAN) among patients with intellectual disability and young-onset parkinsonism., PMID:25744623
Mitochondria: A crossroads for lipid metabolism defect in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation diseases., PMID:25668476
Alteration of the coenzyme A biosynthetic pathway in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation syndromes., PMID:25110004
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: update on pathogenic mechanisms., PMID:24847269
Exome sequence reveals mutations in CoA synthase as a cause of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation., PMID:24360804
EDC4 interacts with and regulates the dephospho-CoA kinase activity of CoA synthase., PMID:22982864
Evaluation of CoA biosynthesis proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as potential drug targets., PMID:22954585
CoA Synthase is phosphorylated on tyrosines in mammalian cells, interacts with and is dephosphorylated by Shp2PTP., PMID:19763791
CoA synthase is in complex with p85alphaPI3K and affects PI3K signaling pathway., PMID:19482007