Catalog No.
YHE91901
Expression system
E. coli
Species
Homo sapiens (Human)
Protein length
Leu243-Gly502
Predicted molecular weight
31.09 kDa
Nature
Recombinant
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
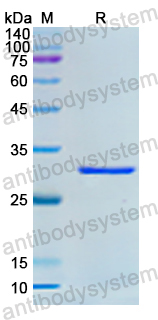
Purity
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Accession
P52429
Applications
ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Form
Lyophilized
Storage buffer
Lyophilized from a solution in PBS pH 7.4, 0.02% NLS, 1mM EDTA, 4% Trehalose, 1% Mannitol.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute in sterile water for a stock solution. A copy of datasheet will be provided with the products, please refer to it for details.
Shipping
In general, proteins are provided as lyophilized powder/frozen liquid. They are shipped out with dry ice/blue ice unless customers require otherwise.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Alternative Names
DGKE, Diglyceride kinase epsilon, DAG kinase epsilon, DGK-epsilon, Diacylglycerol kinase epsilon, DAGK5
Pregnancy-related Thrombotic Microangiopathy has a spectrum of underlying causes., PMID:40306205
Adolescence-onset atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: is it different from infant-onset?, PMID:38704765
Novel Heterozygous Missense Variants in Diacylglycerol Kinase Epsilon and Complement Factor I: Potential Pathogenic Association With Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome., PMID:38374836
Interaction of ROMK2 channel with lipid kinases DGKE and AGK: Potential channel activation by localized anionic lipid synthesis., PMID:38056763
Concurrent Cobalamin C and Plasminogen Deficiencies in a Patient with Chronic Thrombotic Microangiopathy., PMID:37611544
MicroRNA, mRNA, and Proteomics Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Improving Lung Cancer Treatment Outcomes., PMID:37190222
CFH-CFHR1 hybrid genes in two cases of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome., PMID:36755127
Variants in complement genes are uncommon in patients with anti-factor H autoantibody-associated atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome., PMID:36622444
An intact zinc finger motif of the C1B domain is critical for stability and activity of diacylglycerol kinase-ε., PMID:36113832
Diacylglycerol kinase epsilon protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through Krüppel-like factor 15/klotho pathway., PMID:35616094
A novel missense mutation in complement factor I predisposes patients to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: a case report., PMID:35241161
Thrombotic microangiopathy in children., PMID:35041041
Pediatric Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Advances., PMID:34944087
A thermal adaptation landscape related to virulence in Mucor irregularis transcriptional profiles., PMID:34779032
Loss of diacylglycerol kinase ε causes thrombotic microangiopathy by impairing endothelial VEGFA signaling., PMID:33986189
A patient with a homozygous diacylglycerol kinase epsilon (DGKE) gene mutation with atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome and low C3 responded well to eculizumab: a case report., PMID:33879077
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome due to DGKE mutation and response to eculizumab: lessons for the clinical nephrologist., PMID:33751496
Distinct genetic profile with recurrent population-specific missense variants in Korean adult atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome., PMID:33213850
Whole exome sequencing revealed a novel homozygous variant in the DGKE catalytic domain: a case report of familial hemolytic uremic syndrome., PMID:32838746
Genetic and Protein Structural Evaluation of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy., PMID:32553244
Various phenotypes of disease associated with mutated DGKE gene., PMID:32413569
A novel compound heterozygous mutation in DGKE in a Chinese patient causes atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome., PMID:32091318
Reprogramming fatty acyl specificity of lipid kinases via C1 domain engineering., PMID:31932721
Eculizumab treatment of thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with ulcerative colitis., PMID:31612381
Whole-exome sequencing detects mutations in pediatric patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in Taiwan., PMID:30905589
Treatment of hemolytic uremic syndrome related to Bordetella pertussis infection -is plasma exchange or eculizumab use necessary?, PMID:30558570
Genetic Analysis of 400 Patients Refines Understanding and Implicates a New Gene in Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome., PMID:30377230
Membrane curvature allosterically regulates the phosphatidylinositol cycle, controlling its rate and acyl-chain composition of its lipid intermediates., PMID:30237168
Genetic diagnosis of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in a longitudinal collection of Czech and Slovak patients: a high proportion of causative variants in NUP93., PMID:29869118
Statistical Validation of Rare Complement Variants Provides Insights into the Molecular Basis of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy., PMID:29500241
Atypical presentation of atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome., PMID:29440240
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency Mimicking Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome., PMID:29248304
Hemolytic uremic syndrome as the presenting manifestation of WT1 mutation and Denys-Drash syndrome: a case report., PMID:28720077
The Phenotypic Spectrum of Nephropathies Associated with Mutations in Diacylglycerol Kinase ε., PMID:28526779
HUS and atypical HUS., PMID:28416508
Expression, Purification, and Properties of a Human Arachidonoyl-Specific Isoform of Diacylglycerol Kinase., PMID:28199087
Genomic and clinical profiling of a national nephrotic syndrome cohort advocates a precision medicine approach to disease management., PMID:28117080
Defining the genetics of thrombotic microangiopathies., PMID:27177491
Testing the Activity of Complement Convertases in Serum/Plasma for Diagnosis of C4NeF-Mediated C3 Glomerulonephritis., PMID:27146825
[Genetics of aHUS and transplant recurrence]., PMID:26479051
Molecular properties of diacylglycerol kinase-epsilon in relation to function., PMID:26134136
Atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome in a Japanese patient with DGKE genetic mutations., PMID:26018111
Characterization of a New DGKE Intronic Mutation in Genetically Unsolved Cases of Familial Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome., PMID:25854283
[Atypical HUS caused by complement-related abnormalities]., PMID:25765799
DGKE disruption ditches complement and drives p38 signaling., PMID:25655457
Podocyte dysfunction in atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome., PMID:25599621
Loss of DGKε induces endothelial cell activation and death independently of complement activation., PMID:25498910
[Pathogenesis and clinical features of HUS * aHUS]., PMID:25420405