Catalog No.
RHJ81301
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Host species
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Clonality
Monoclonal
Tested applications
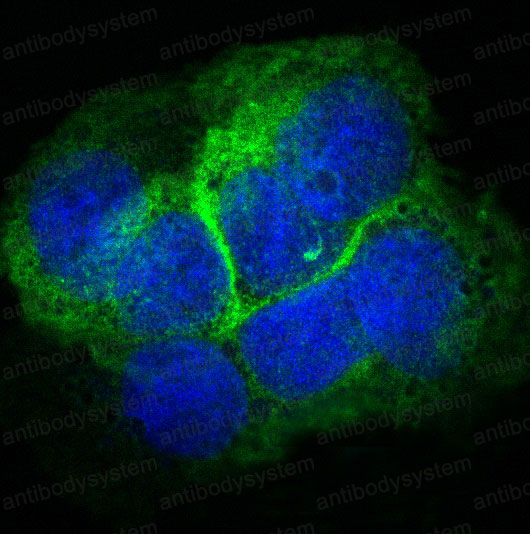
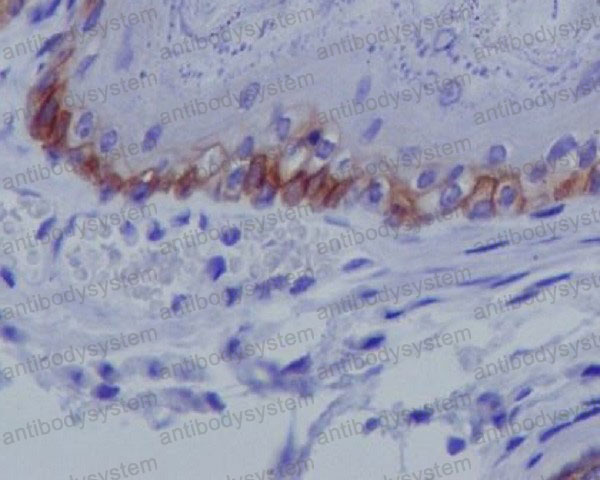
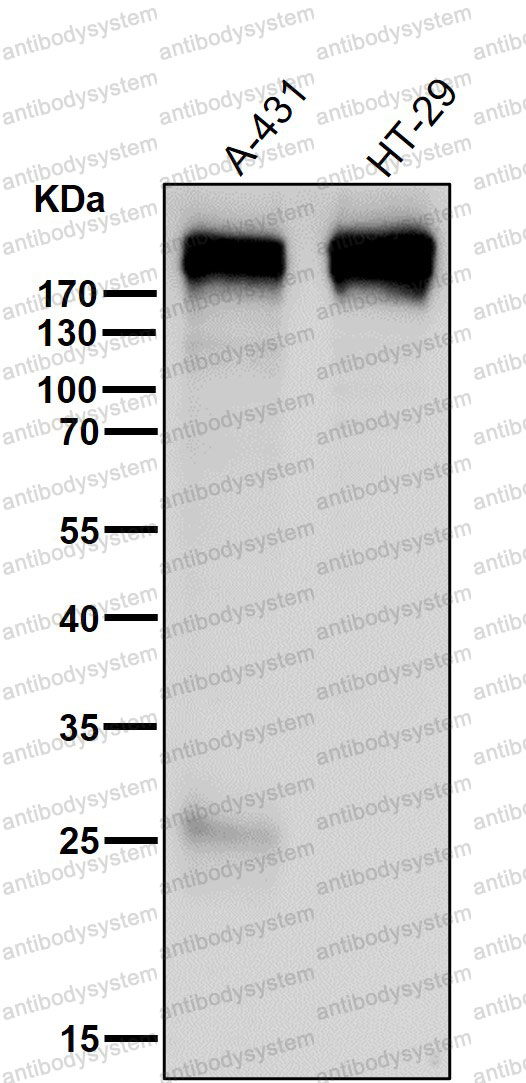
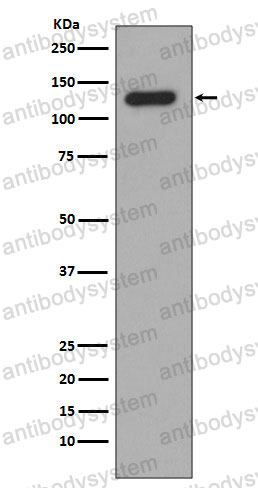
IF: 1:50-1:200, IHC: 1:100-1:200, IP: 1:20-1:50, WB: 1:1000-1:2000
Target
BP180, BPA 2, BPAG2, COL17A1, Collagen 17, CollagenXVII, LAD1, Collagen XVII alpha 1
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
Purity
>95% by SDS-PAGE.
Purification
Protein A/G purified from cell culture supernatant.
Accession
Q9UMD9
Applications
IF, IHC, IP, WB
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4, 0.05% BSA, 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Sodium azide.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Store at +4 ℃ short term (1-2 weeks).
Store at -20 ℃ 12 months.
Store at -80 ℃ long term.
Clone ID
R1C32
Native Autoantigen Complex Detects Pemphigoid Autoantibodies., PMID:36992950
Absence of NC14A Domain of COLXVII/BP180 in Mice Results in IL-17‒Associated Skin Inflammation., PMID:35985497
The CD44/COL17A1 pathway promotes the formation of multilayered, transformed epithelia., PMID:34087104
Small molecule Y-320 stimulates ribosome biogenesis, protein synthesis, and aminoglycoside-induced premature termination codon readthrough., PMID:33939688
Identification of a Novel COL17A1 Compound Heterozygous Mutation in a Chinese Girl with Non-Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa., PMID:32862392
Tetraspanin CD151 and integrin α3β1 contribute to the stabilization of integrin α6β4-containing cell-matrix adhesions., PMID:31488507
Life before and beyond blistering: The role of collagen XVII in epidermal physiology., PMID:29604146
New versatile monoclonal antibodies against type XVII collagen endodomain for diagnosis and subtyping COL17A1-associated junctional epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:26334130
Dermal eosinophilic infiltrate in junctional epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:25950805
Collagen XVII is expressed in malignant but not in benign melanocytic tumors and it can mediate antibody induced melanoma apoptosis., PMID:22688676
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa of late onset explained by mutations in COL17A1., PMID:21466533
Bullous pemphigoid in a patient with suspected non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:20456391
Localized and generalized forms of blistering in junctional epidermolysis bullosa due to COL17A1 mutations in the Netherlands., PMID:17263807
Eosinophil infiltration in three patients with generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa from a Japanese family: molecular genetic and immunohistochemical studies., PMID:16172808
A novel homozygous point mutation in the COL17A1 gene in a Chinese family with generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:11912005
Deletion of the cytoplasmatic domain of BP180/collagen XVII causes a phenotype with predominant features of epidermolysis bullosa simplex., PMID:11851893
Truncated typeXVII collagen expression in a patient with non-herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa caused by a homozygous splice-site mutation., PMID:11406649
The 97 kDa linear IgA bullous dermatosis antigen is not expressed in a patient with generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa with a novel homozygous G258X mutation in COL17A1., PMID:9804354
Two forms of collagen XVII in keratinocytes. A full-length transmembrane protein and a soluble ectodomain., PMID:9748270
Cloning of the human type XVII collagen gene (COL17A1), and detection of novel mutations in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:9012408
Generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:9551142
Compound heterozygosity for a dominant glycine substitution and a recessive internal duplication mutation in the type XVII collagen gene results in junctional epidermolysis bullosa and abnormal dentition., PMID:8669466