Catalog No.
YVV20303
Expression system
E. coli
Species
Human enterovirus 71 (strain 7423/MS/87) (EV71) (EV-71)
Protein length
Gly2-Lys69
Predicted molecular weight
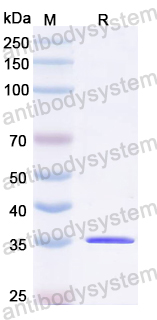
35.54 kDa
Nature
Recombinant
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
Purity
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Accession
Q66479
Applications
ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Form
Lyophilized
Storage buffer
Lyophilized from a solution in PBS pH 7.4, 0.02% NLS, 1mM EDTA, 4% Trehalose, 1% Mannitol.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute in sterile water for a stock solution. A copy of datasheet will be provided with the products, please refer to it for details.
Shipping
In general, proteins are provided as lyophilized powder/frozen liquid. They are shipped out with dry ice/blue ice unless customers require otherwise.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for one week. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Alternative Names
Genome polyprotein, Capsid protein VP4, P1A, Virion protein 4
Cell membrane-bound toll-like receptor-1/2/4/6 monomers and -2 heterodimer inhibit enterovirus 71 replication by activating the antiviral innate response., PMID:37207203
The upregulation of peripheral blood polyamine metabolites spermidine and spermine in children with hand, foot, mouth disease is related to enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1, but not VP4., PMID:36891375
Chimeric enterovirus 71 virus-like particle displaying conserved coxsackievirus A16 epitopes elicits potent immune responses and protects mice against lethal EV71 and CA16 infection., PMID:34116877
Human Antibodies to VP4 Inhibit Replication of Enteroviruses Across Subgenotypes and Serotypes, and Enhance Host Innate Immunity., PMID:33101238
N6-methyladenosine modifications enhance enterovirus 71 ORF translation through METTL3 cytoplasmic distribution., PMID:32446384
Myristoylation of EV71 VP4 is Essential for Infectivity and Interaction with Membrane Structure., PMID:32399947
The surveillance of the epidemiological and serotype characteristics of hand, foot, mouth disease in Neijiang city, China, 2010-2017: A retrospective study., PMID:31170178
Induction of immune responses by a novel recombinant fusion protein of enterovirus A71 in BALB/c mice., PMID:30465931
Structure, Immunogenicity, and Protective Mechanism of an Engineered Enterovirus 71-Like Particle Vaccine Mimicking 80S Empty Capsid., PMID:29070691
Glucocorticoids Prevent Enterovirus 71 Capsid Protein VP1 Induced Calreticulin Surface Exposure by Alleviating Neuronal ER Stress., PMID:27848175
Inhibition of enterovirus VP4 myristoylation is a potential antiviral strategy for hand, foot and mouth disease., PMID:27520386
EV71 virus-like particles produced by co-expression of capsid proteins in yeast cells elicit humoral protective response against EV71 lethal challenge., PMID:26809443
Identification of Positively Charged Residues in Enterovirus 71 Capsid Protein VP1 Essential for Production of Infectious Particles., PMID:26512078
Prevalence of Coxsackievirus A6 and Enterovirus 71 in Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Nanjing, China in 2013., PMID:26090576
Phage Display-Derived Cross-Reactive Neutralizing Antibody against Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16., PMID:26073737
Development of a stable Gaussia luciferase enterovirus 71 reporter virus., PMID:25843263
Immunization of N terminus of enterovirus 71 VP4 elicits cross-protective antibody responses., PMID:24320792
VP2 dominated CD4+ T cell responses against enterovirus 71 and cross-reactivity against coxsackievirus A16 and polioviruses in a healthy population., PMID:23863902
[2009 evolution for VP4 of enterovirus 71 strains in Shenzhen]., PMID:23855119
Functional comparison of SCARB2 and PSGL1 as receptors for enterovirus 71., PMID:23302872
Development and characterization of a stable eGFP enterovirus 71 for antiviral screening., PMID:23267829
Immunological and biochemical characterization of coxsackie virus A16 viral particles., PMID:23226233
Characterization of enterovirus 71 capsids using subunit protein-specific polyclonal antibodies., PMID:23046991
Epidemiological and etiological characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Ningbo, China, 2008-2011., PMID:22652041
Comparing Enterovirus 71 with Coxsackievirus A16 by analyzing nucleotide sequences and antigenicity of recombinant proteins of VP1s and VP4s., PMID:22050722
[Sequence and antigenicity analysis for VP4s of EV71 strains isolated from Children in Beijing]., PMID:21774244
Purification and characterization of enterovirus 71 viral particles produced from vero cells grown in a serum-free microcarrier bioreactor system., PMID:21603631
Phylogenetic designation of enterovirus 71 genotypes and subgenotypes using complete genome sequences., PMID:19465162
[Genotype analysis of enterovirus type 71 detected from patients with hand-foot-mouth disease in Shenzhen]., PMID:19103116
[Rapid enterovirus genotyping in cerebrospinal fluids: a two-year prospective study in a virology laboratory setting]., PMID:18835107
Enterovirus 71 in Taiwan, 2004-2006: epidemiological and virological features., PMID:18584550
Appearance of intratypic recombination of enterovirus 71 in Taiwan from 2002 to 2005., PMID:18036697
The VP1 structural protein of enterovirus 71 interacts with human ornithine decarboxylase and gene trap ankyrin repeat., PMID:17276651
The VP1 protein of human enterovirus 71 self-associates via an interaction domain spanning amino acids 66-297., PMID:16555287
Evolution of EV71 genogroup in Taiwan from 1998 to 2005: an emerging of subgenogroup C4 of EV71., PMID:16372302
Revealing molecular targets for enterovirus type 71 detection by profile hidden Markov models., PMID:16175339