Renewed Nipah Virus Outbreak in India
Recent reports of Nipah virus (NiV) infections in India have once again drawn global attention to this highly lethal zoonotic pathogen. Despite its relatively low incidence, NiV is associated with case fatality rates of up to 75%, strong neurotropism, and the absence of licensed vaccines or specific antiviral therapies.
As a result, Nipah virus remains a WHO priority pathogen, requiring sustained efforts in fundamental virology, immunology, and diagnostic development.
Molecular Features Driving Nipah Virus Pathogenicity
Nipah virus is an enveloped, negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus Henipavirus. Its ~18.2 kb genome encodes multiple structural and non-structural proteins that support efficient replication and immune evasion.
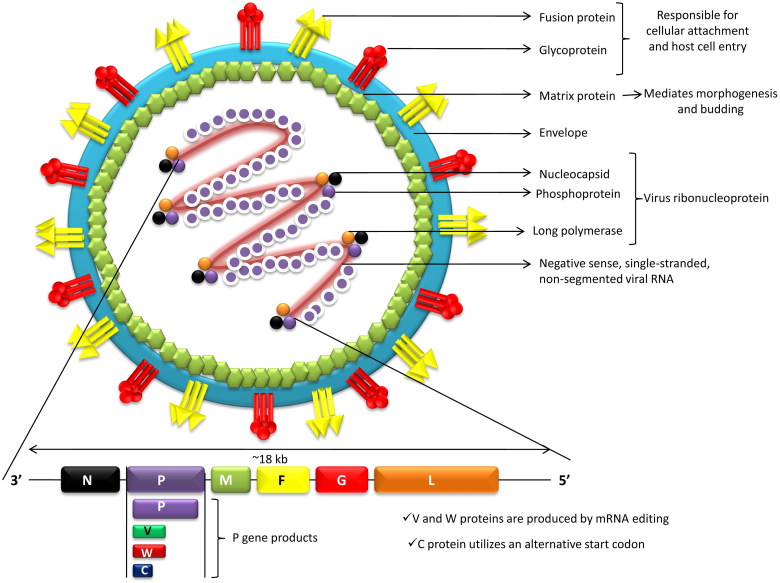
Key Viral Proteins
G (attachment) and F (fusion) glycoproteins mediate viral entry via ephrin-B2/B3 receptors and represent the primary targets for neutralizing antibodies and vaccine development.
N, P, and M proteins orchestrate viral replication, assembly, and inclusion body formation, making them indispensable targets for mechanistic studies.
These molecular characteristics underpin the virus's broad host range, endothelial tropism, and ability to breach the blood-brain barrier.
Transmission of Nipah Virus
Nipah virus is a zoonotic pathogen with fruit bats (Pteropus species) serving as its primary natural reservoir. Spillover to humans occurs through direct contact with bat-contaminated food or environments, as well as via intermediate animal hosts such as pigs, which can efficiently amplify viral transmission.
Importantly, Nipah virus is also capable of human-to-human transmission, primarily through close contact with respiratory secretions, saliva, urine, or other bodily fluids of infected individuals. Such transmission has been documented particularly in household and healthcare settings, underscoring the risk of localized outbreaks. The virus can remain viable in the environment for several days, further increasing the potential for indirect exposure.
Pathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection
Nipah virus initiates infection by binding of its surface G glycoprotein to ephrin-B2 and ephrin-B3 receptors, which are widely expressed on endothelial cells and neurons. This interaction triggers conformational changes that activate the viral F fusion protein, enabling membrane fusion and viral genome entry into host cells.
Following entry, Nipah virus replicates efficiently within host cells and expresses multiple non-structural proteins that antagonize innate immune responses, particularly by inhibiting STAT1 and STAT2 signaling pathways. This immune evasion allows rapid viral dissemination during early stages of infection.
Clinically, Nipah virus exhibits pronounced endothelial and neurotropism, leading to systemic vasculitis, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, and acute or delayed-onset encephalitis. In addition, infection of the respiratory tract can result in severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). These pathological features collectively account for the high mortality and long-term neurological sequelae observed in survivors.
Research Challenges
With no approved vaccines or antiviral drugs available, current NiV research focuses on:
- Viral entry and membrane fusion mechanisms
- Immune evasion strategies
- Antibody and vaccine candidate development
- Serological assay design
All of these research directions rely heavily on high-quality recombinant viral proteins and well-characterized antibodies.
Vaccine platforms for NiV (DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2019.1580827)
AntibodySystem Solutions for Nipah Virus Research
AntibodySystem offers a comprehensive portfolio of research-grade Nipah virus recombinant proteins, antibodies, and ELISA kits, covering key viral targets such as G, F, N, and M proteins.
These tools support a wide range of applications, including:
- Viral entry and neutralization studies
- Replication and assembly mechanism analysis
- Immunological and serological assay development
Recombinant Protein
| Catalog | Product Name |
|---|---|
| EVV07901 | Recombinant Nipah virus G protein/Glycoprotein G Protein, C-His |
| EVV08101 | Recombinant Nipah virus/HeV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Protein, C-His |
| YVV07901 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV G protein/Glycoprotein G Protein, N-His |
| YVV18501 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV M/Matrix Protein, N-His |
| YVV16602 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV Protein N/Nucleoprotein Protein, N-His-SUMO & C-Strep |
| YVV08101 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Protein, N-His-SUMO & C-Strep |
| YVV16601 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV Protein N/Nucleoprotein Protein, N-His |
| YVV08102 | Recombinant Nipah virus/NiV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Protein, N-His |
Antibody
| Catalog | Product Name |
|---|---|
| PVV18501 | Anti-Nipah virus M/Protein M Polyclonal Antibody |
| PVV08101 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Polyclonal Antibody |
| PVV07901 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV G protein/Glycoprotein G Polyclonal Antibody |
| PVV16601 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV Protein N/Nucleoprotein Polyclonal Antibody |
| VVV08103 | InVivoMAb Anti-Nipah virus/NiV Prefusion Antibody (1A9) |
| VVV08101 | InVivoMAb Anti-Nipah virus/NiV Prefusion Antibody (4H3) |
| VVV08105 | InVivoMAb Anti-Nipah virus/NiV Prefusion Protein Antibody (2B12) |
ELISA Kits
| Catalog | Product Name |
|---|---|
| KAV07901 | Anti-Nipah virus/NiV Glycoprotein hIgG ELISA Kit |
| KVV07901 | Nipah virus/NiV Glycoprotein ELISA Kit |
Research Citations
AntibodySystem NiV antibodies have been cited in recent publications from leading institutions, including the Institute of Virology, Philipps University Marburg and the University of Tokyo:
Cell-cell fusion limits activation of the unfolded protein response induced by the Nipah virus glycoproteins
Author information: Institute of Virology, Philipps University Marburg
Cited Product:
| Catalog | Product Name |
| PVV16601 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV Protein N/Nucleoprotein Polyclonal Antibody |
Western Blot from the study
Coordinated interactions among Nipah virus N, P and M proteins drive formation of distinct inclusion bodies
Author information: The University of Tokyo
Cited Products:
| Catalog | Product Name |
| PVV08101 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Polyclonal Antibody |
| PVV07901 | Anti-Nipah virus/HeV G protein/Glycoprotein G Polyclonal Antibody |

Immunofluorescence from the study
