Catalog No.
KDH02203
Description
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
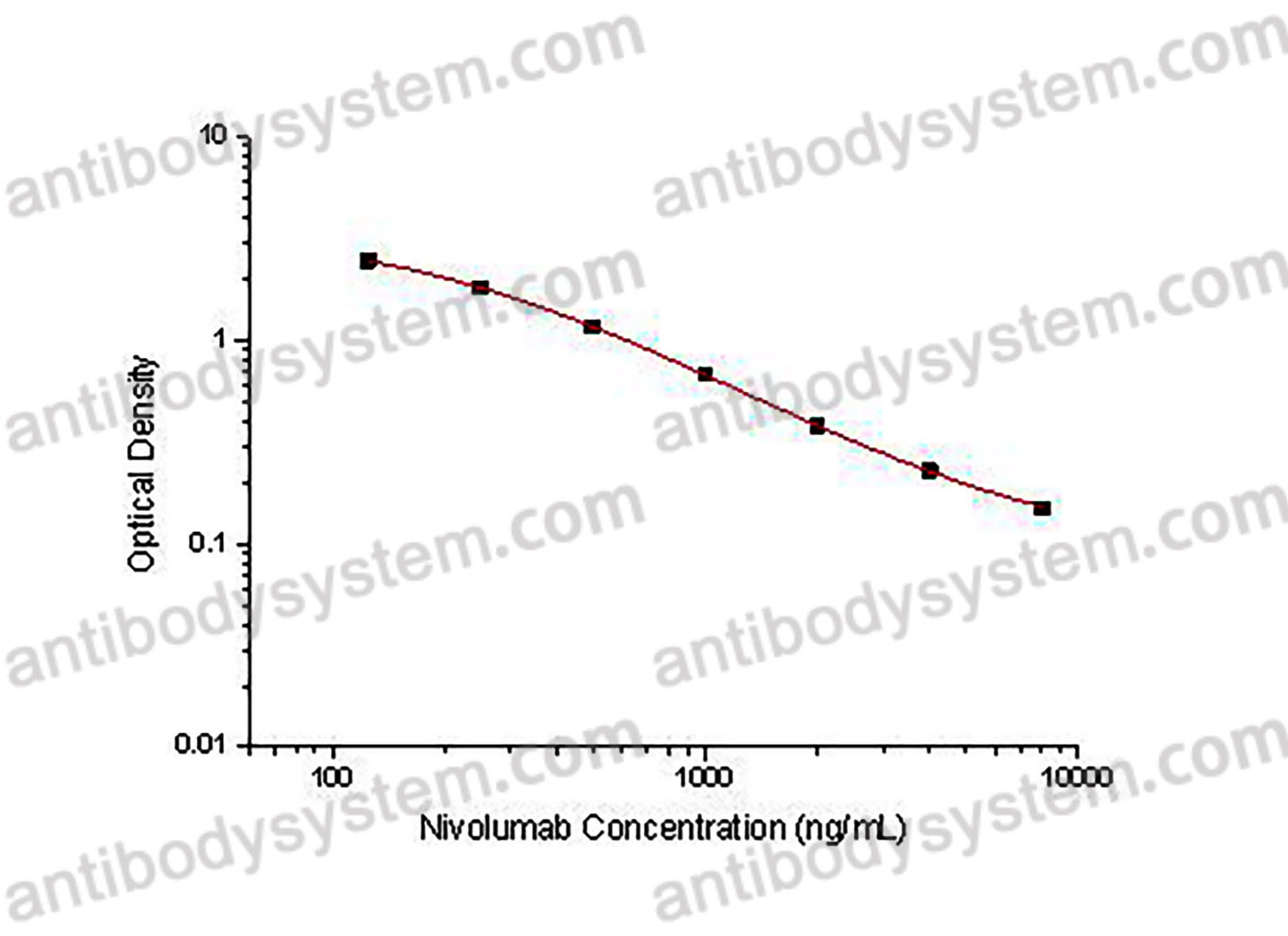
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant human PD1 antigen has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Nivolumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Nivolumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Nivolumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Nivolumab concentration in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatant.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
125 - 8,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
29.40 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
5466.0
|
1320.0
|
302.6
|
6175.7
|
1584.3
|
314.6
|
|
Standard deviation
|
331.7
|
77.8
|
18.0
|
334.9
|
144.2
|
46.9
|
|
CV (%)
|
6.1
|
5.9
|
5.9
|
5.4
|
9.1
|
14.9
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
BMS-936558, MDX-1106, ONO-4538, CAS: 946414-94-4
Background
Nivolumab is a human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that binds to the programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) receptor and selectively blocks interaction with its programmed death ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors and signalling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumour tissue. The inhibitory effect of PD-1 and its ligands occurs through the promotion of apoptosis in antigen specific T cells while simultaneously blocking apoptosis in suppressor T cells. Blocking PD-1 activity has been shown to lead to decreased tumour growth in mouse tumour models.
Phase II study of rucaparib and nivolumab in patients with leiomyosarcoma., PMID:40514070
Time toxicity of nivolumab in metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients: a single-institution experience., PMID:40514043
Expanding access to cancer immunotherapy: A systematic review of low-dose PD-(L)1 inhibitor strategies., PMID:40513286
Nivolumab plus relatlimab in advanced melanoma: RELATIVITY-047 4-year update., PMID:40513285
Impaired Overall Survival of Melanoma Patients Due to Antibiotic Use Prior to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis., PMID:40507352
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Advanced Melanoma in Older Patients: An Overview of Published Data., PMID:40507314
Single-Center Cohort of Pediatric Patients with High-Risk Neuroblastoma Receiving Immunotherapy., PMID:40507305
Baseline Radiomics as a Prognostic Tool for Clinical Benefit from Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Inoperable NSCLC Without Activating Mutations., PMID:40507271
Tight competition for the first line treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma: a comprehensive review of practice-changing developments in recent years., PMID:40506833
Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy improves overall survival in resectable NSCLC., PMID:40506587
Combined immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab with and without sequential or concomitant stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with melanoma brain metastasis: An international retrospective study., PMID:40505525
Treatment of older patients with Hodgkin lymphoma., PMID:40504313
Case Report: Locally invasive thyroid metastases from renal cell carcinoma: surgery after neoadjuvant therapy., PMID:40502628
NEXUS: a phase I dose escalation study of selinexor plus nivolumab and ipilimumab in Asian patients with advanced/metastatic solid malignancies., PMID:40502306
Engraftment Syndrome Following Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in a Patient Receiving Nivolumab as Salvage Therapy., PMID:40497705
Obesity paradox role in the immunosuppressive treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40497086
Enfortumab vedotin induced interstitial lung disease: A first case report with pathological evidence from transbronchial lung cryobiopsy., PMID:40496844
Drug-associated abdominal aortitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis after treatment with nivolumab., PMID:40496660
The real-world safety of Nivolumab: a pharmacovigilance analysis based on the FDA adverse event reporting system., PMID:40491923
Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma Treated With Nivolumab., PMID:40489108
Biomarker analysis and treatment dynamics following preoperative ipilimumab plus nivolumab in locally advanced urothelial cancer from the phase 1B NABUCCO study., PMID:40489082
Implementing performance-based risk-sharing agreements in non-small cell lung cancer immunotherapy: a real-world data case study., PMID:40489036
Organ-Specific Responses to Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study., PMID:40488227
Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma of the Stomach with Chylous Pleural Effusion: Laterality Shift and Fluid Composition Change., PMID:40487559
Safety and short-term outcomes of adjuvant nivolumab therapy at 480 mg dose every four weeks in resected esophageal cancer: a prospective cohort study., PMID:40484886
Cost-Utility and Budget Impact Analysis of Immunotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Kidney Cancer in Latin America: Evidence From Uruguay., PMID:40482312
Validation of a 15-Gene Prognostic Signature in Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma., PMID:40479621
A multicenter Phase II study of mFOLFOX6 plus nivolumab for gastric cancer with severe peritoneal metastases: WJOG16322G., PMID:40476844
"Attenuated" Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy on Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment: A Case Report., PMID:40475293
A phase II study of nivolumab, ipilimumab, and radiation in combination with influenza vaccine in patients with pancreatic cancer (INFLUENCE)., PMID:40475164
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: tumour response and immune-related renal vasculitis following cytoreductive nephrectomy., PMID:40474803
Cell-mediated mucositis of the oral cavity: narrative review on etiology, clinico-pathological aspects and malignant transformation., PMID:40474707
Inherited mitochondrial genetics as a predictor of immune checkpoint inhibition efficacy in melanoma., PMID:40473950
Assessing individual head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patient response to therapy through integration of functional and genomic data., PMID:40473660
Treatment-Free Survival Over 6 Years of Follow-up in Patients With Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus Chemotherapy in CheckMate 227 Part 1., PMID:40473108
Phase II trial dedicated to non-selected, pretreated cutaneous angiosarcoma: Efficacy of nivolumab (AngioCheck Study)., PMID:40472568
Nivolumab Induces Durable Remission in Relapsed/Refractory ALK-Negative ALCL After Allogeneic Blood Stem Cell Transplantation-A Case Report and Literature Review., PMID:40469417
Risk factors for checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis., PMID:40469302
Peripheral memory B cell population maintenance and long-term survival after perioperative chemoimmunotherapy in NSCLC (NADIM trial)., PMID:40468805
Immune-mediated enterocolitis is associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A pharmacovigilance study from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database., PMID:40465755
Successful use of nivolumab and relatlimab as salvage therapy for metastatic uveal melanoma., PMID:40465233
Impact of medications on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer., PMID:40465127
Personalized drug stratification using endoscopic samples to assess ex vivo gastric cancer tissue susceptibility to chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors., PMID:40465055
Malignant mesothelioma with a novel BAP1 germline frameshift mutation treated with dual immune checkpoint inhibitors: A case report., PMID:40463358
Primary Vaginal Melanoma or Clear Cell Sarcoma: A Difficult Differential Diagnosis., PMID:40462828
Claudin-18 isoform 2-specific CAR T-cell therapy (satri-cel) versus treatment of physician's choice for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (CT041-ST-01): a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial., PMID:40460847
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for patients with resectable stage III/IV cutaneous melanoma - A Swedish retrospective real-world study (NEO-MEL)., PMID:40456667
Cutaneous adverse effects of combination epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy., PMID:40455297
Overall Survival with Neoadjuvant Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy in Lung Cancer., PMID:40454642
Surgical Management of Destructive Thyroiditis Triggered by Neoadjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report., PMID:40454085